VS Code
Overview
Quarto can render Jupyter notebooks represented as plain text (.qmd) or as a normal notebook file (.ipynb). The Quarto VS Code Extension includes many tools that enhance working these documents, including:
- Integrated render and preview for Quarto documents.
- Syntax highlighting for markdown and embedded languages
- Completion and diagnostics for YAML options
- Completion for embedded languages (e.g. Python, R, Julia, etc.)
- Commands and key-bindings for running cells and selected lines.
- Live preview for LaTeX math as well as Mermaid and Graphviz diagrams
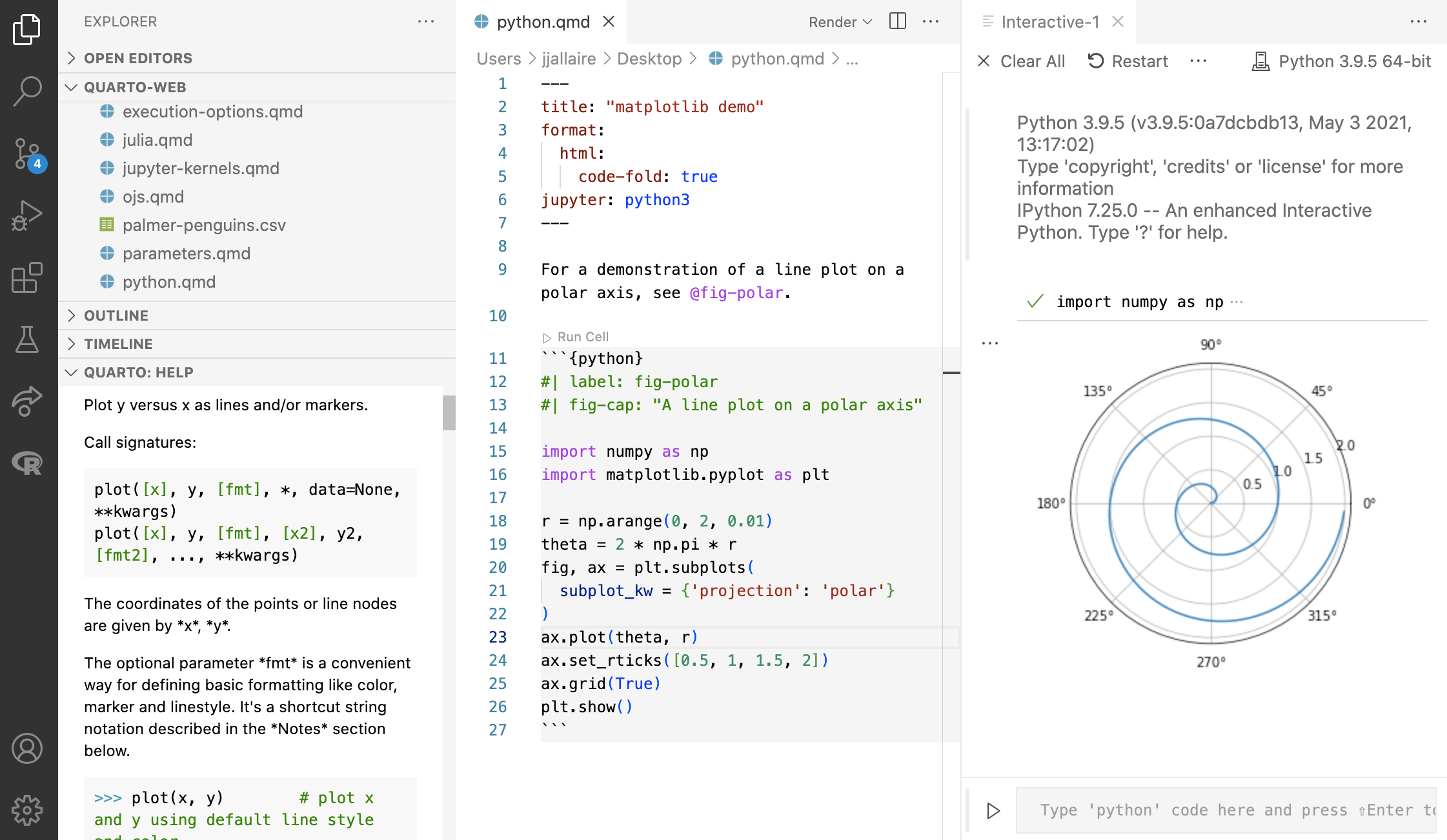
The Quarto extension integrates directly with the Jupyter, R, and Julia extensions. For example, here the Quarto extension runs a Python cell and shows contextual help for Python functions:
Installation
You can install the Quarto extension from the VS Code Extension Marketplace, the Open VSX Registry or directly from a VISX extension file.
Render and Preview
The Quarto VS Code extension includes commands and keyboard shortcuts for rendering Quarto documents (both standalone and within websites or books). After rendering, quarto preview is used behind the scenes to provide a preview pane within VS Code alongside your document:
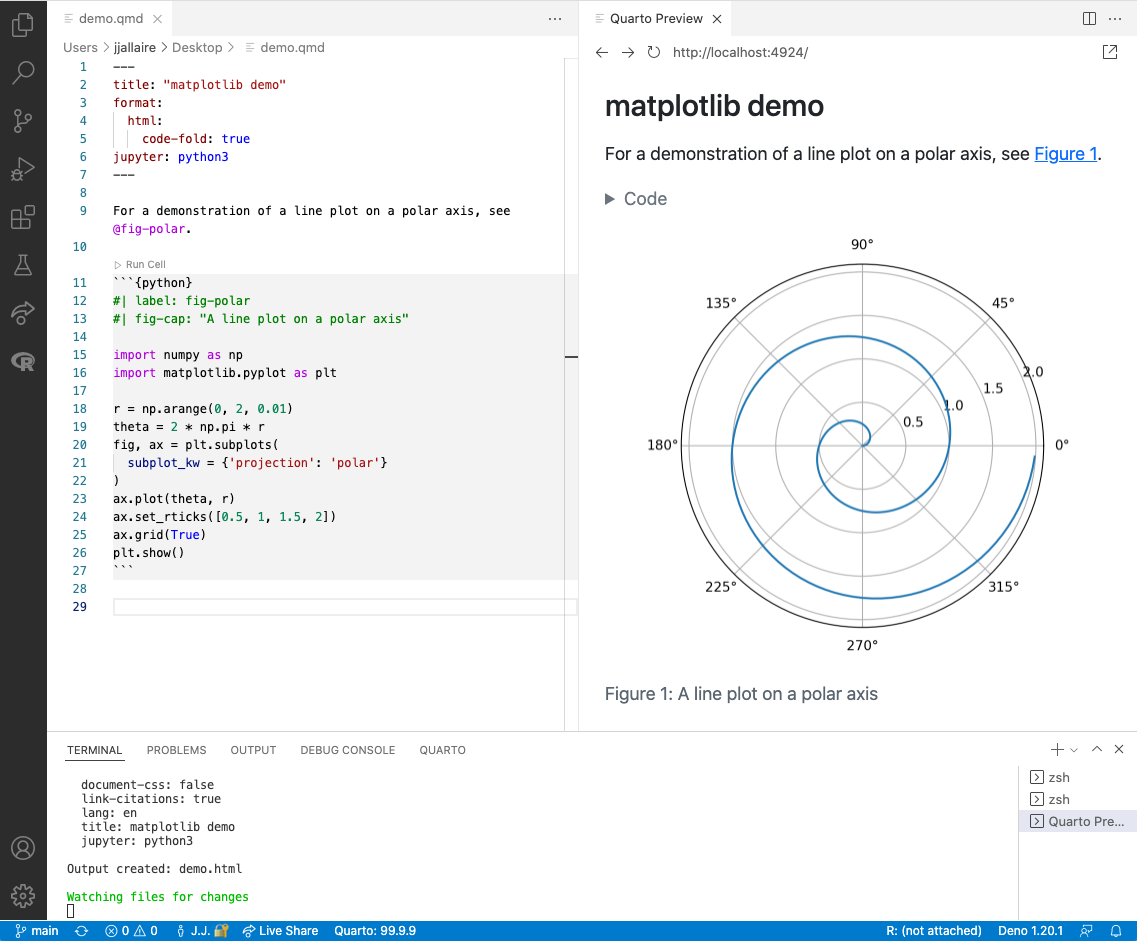
To render and preview, execute the Quarto: Render command. You can alternatively use the Ctrl+Shift+K keyboard shortcut, or the Render button at the top right of the editor:

Note that on the Mac you should use Cmd rather than Ctrl as the prefix for all Quarto keyboard shortcuts.
Additionally, there are commands available to render specific formats. Here is a complete list of the supported render commands:
- Quarto: Render
- Quarto: Render HTML
- Quarto: Render PDF
- Quarto: Render Word
The Quarto: Render command renders the default format of the currently active document. The other commands render specific formats (regardless of the document’s default format). The Ctrl+Shift+K keyboard shortcut will re-execute the most recently executed render command.
Embedded preview is currently supported for HTML and PDF based formats (including revealjs and beamer slideshows). However, for Word and other formats you need to use an appropriate external program to preview the output.
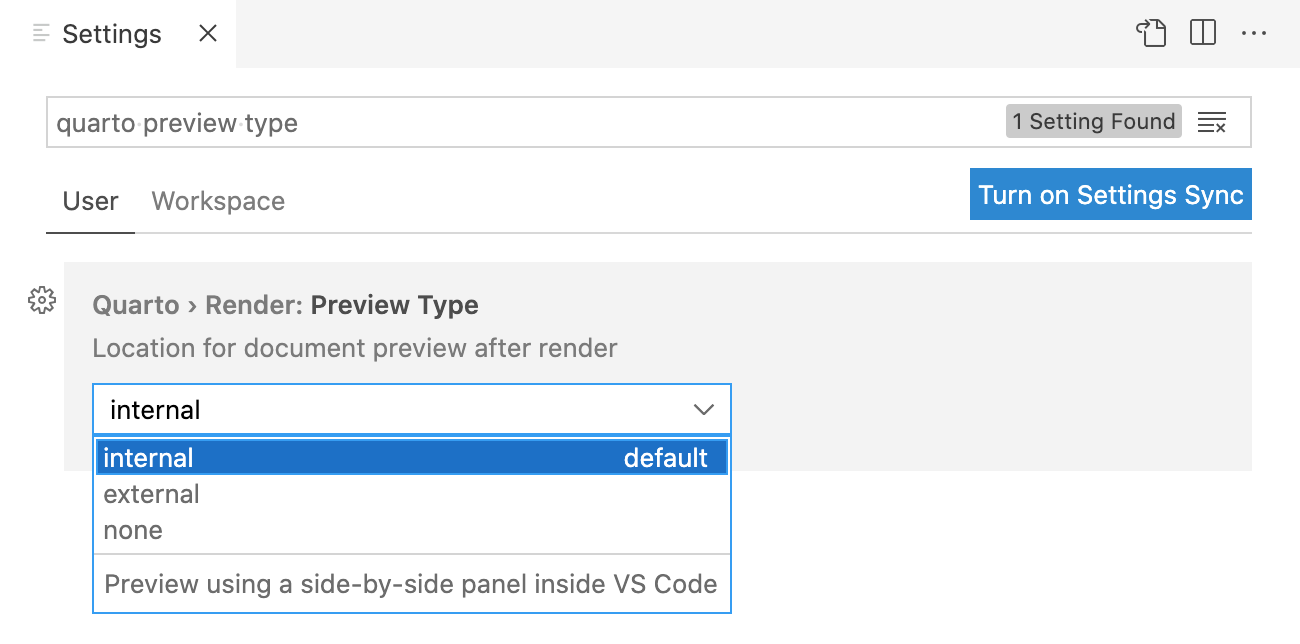
External Preview
If you prefer to use an external browser for preview (or have no preview triggered at all by rendering) you can use the Preview Type option to specify an alternate behavior:
Code Cells
There are a variety of tools that make it easier to edit and execute code cells. Editing tools include syntax highlighting, code folding, code completion, and signature tips:
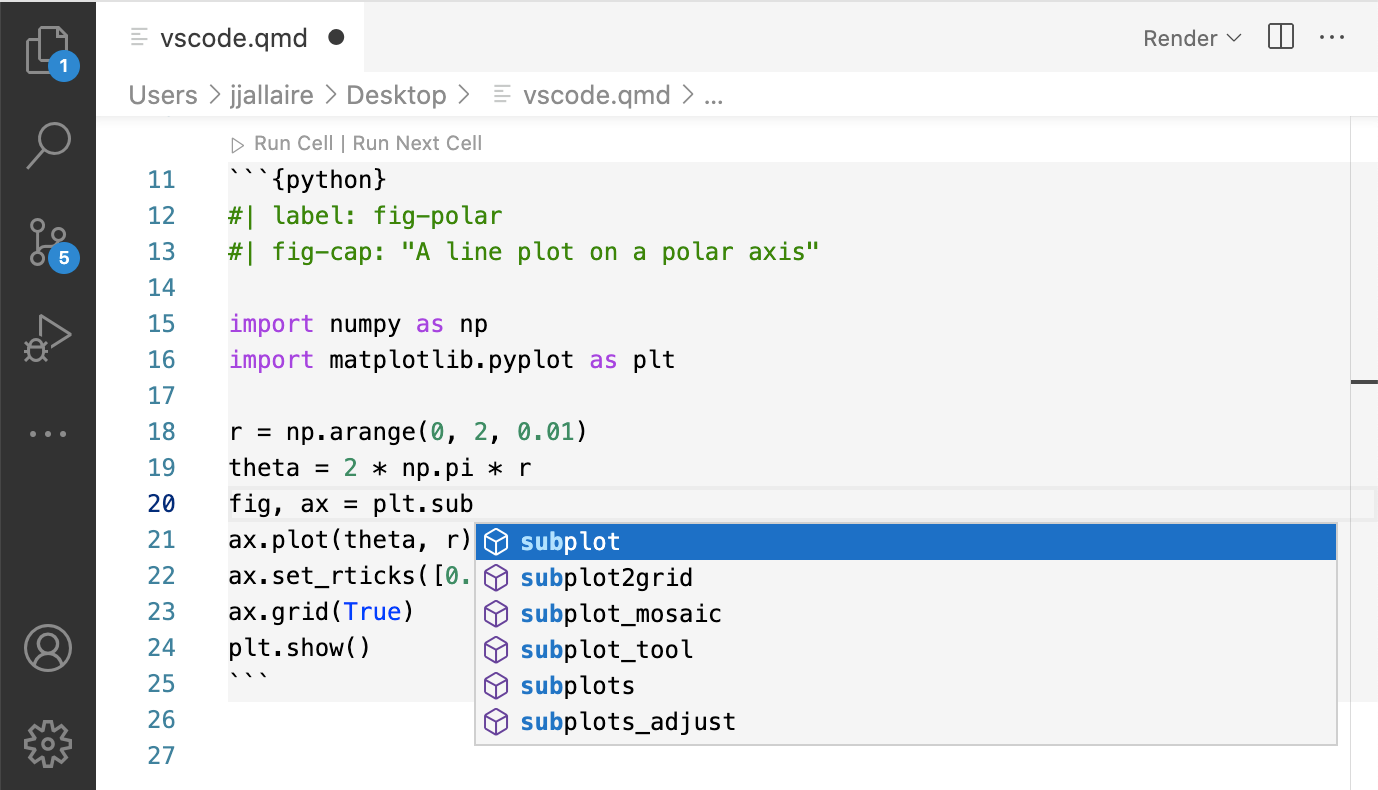
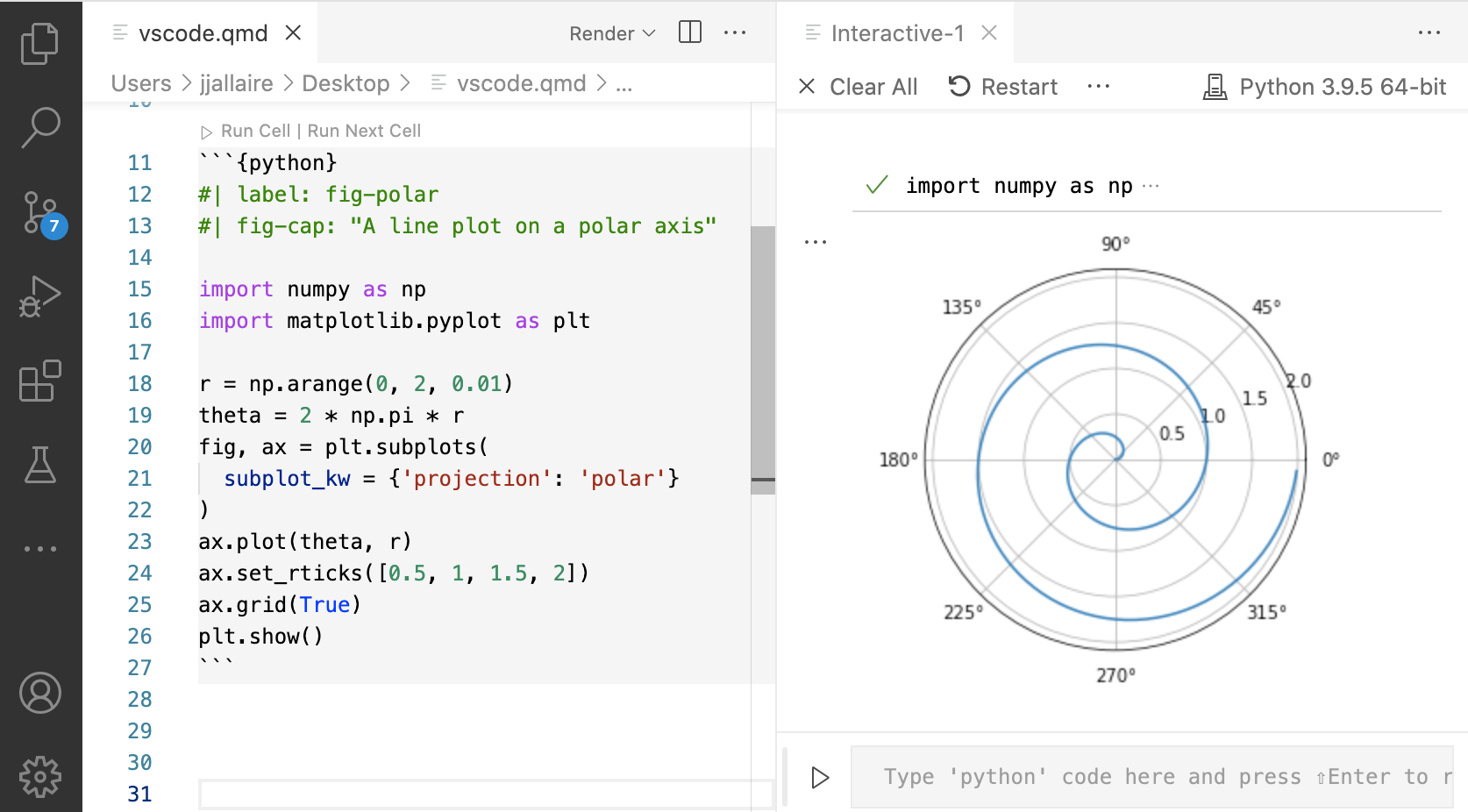
For Python, R, and Julia cells, commands are available to execute the current cell, previous cells, or the currently selected line(s). Cell output is shown side by side in the Jupyter interactive console:
Here are all of the commands and keyboard shortcuts available for executing cells:
| Quarto Command | Keyboard Shortcut |
|---|---|
| Run Current Cell | ⇧⌃ Enter |
| Run Selected Line(s) | ⌃ Enter |
| Run Next Cell | ⌥⌃ N |
| Run Previous Cell | ⌥⌃ P |
| Run All Cells | ⌥⌃ R |
| Run Cells Above | ⇧⌥⌃ P |
| Run Cells Below | ⇧⌥⌃ N |
Enhanced features for embedded languages (e.g. completion, code execution) can be enabled by installing the most recent version(s) of these extensions:
Note that you can quickly insert a new code cell using the Ctrl+Shift+I keyboard shortcut.
Contextual Assistance
Execute the Quarto: Show Assist Panel command to show a panel in the sidebar that shows contextual assistance depending on the current cursor location:
- Help/documentation is shown when editing code
- A realtime preview of equations is shown when editing LaTeX math
- Thumbnail previews are shown when your cursor is located on a markdown image.
For example, below help on the matplotlib plot() function is shown automatically when the cursor is located on the function:

Live Preview
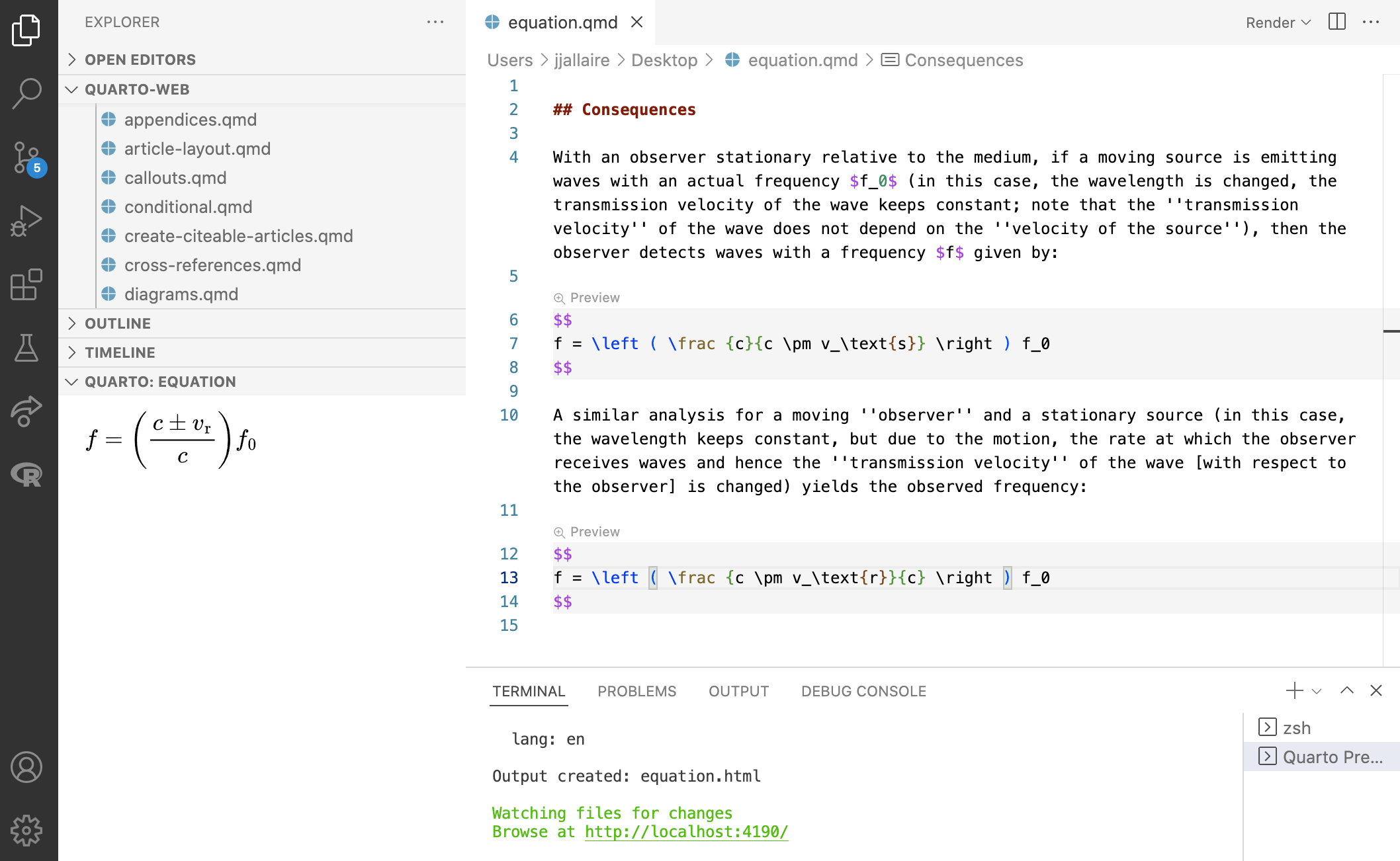
While editing LaTeX math or Mermaid and Graphviz diagrams, click the Preview button above the code (or use the Ctrl+Shift+L keyboard shortcut) to open a live preview which will update automatically as you edit.
Here we see a preview of the currently edited LaTeX equation displayed in the Quarto assist panel:
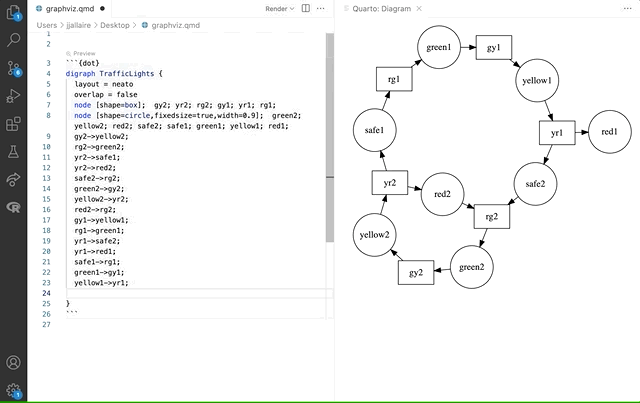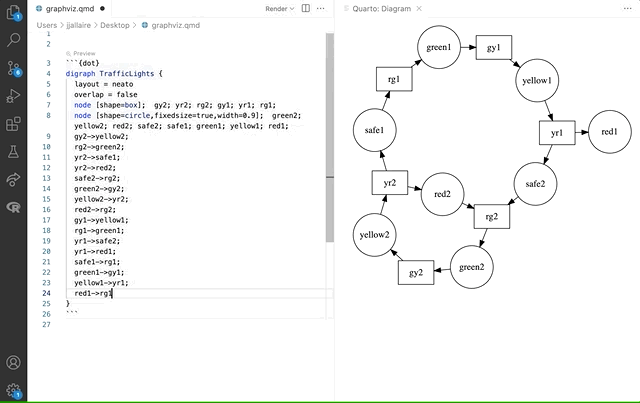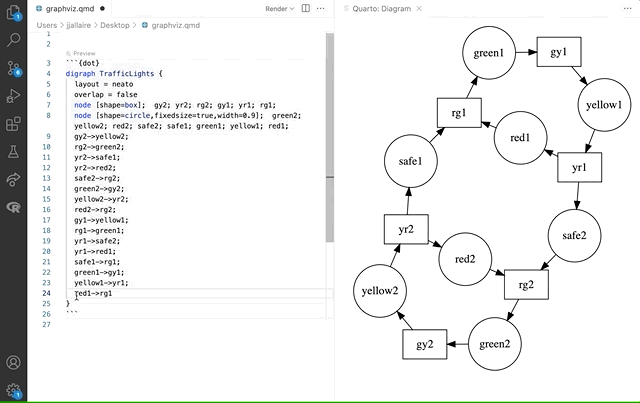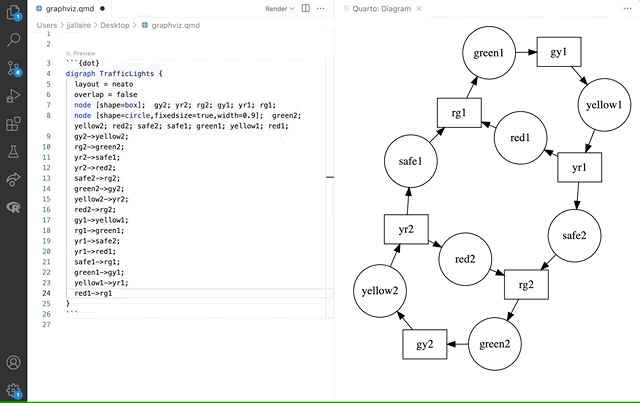
Here we see a Graphviz diagram preview automatically updated as we edit:
YAML Intelligence
YAML code completion is available for project files, YAML front matter, and executable cell options:
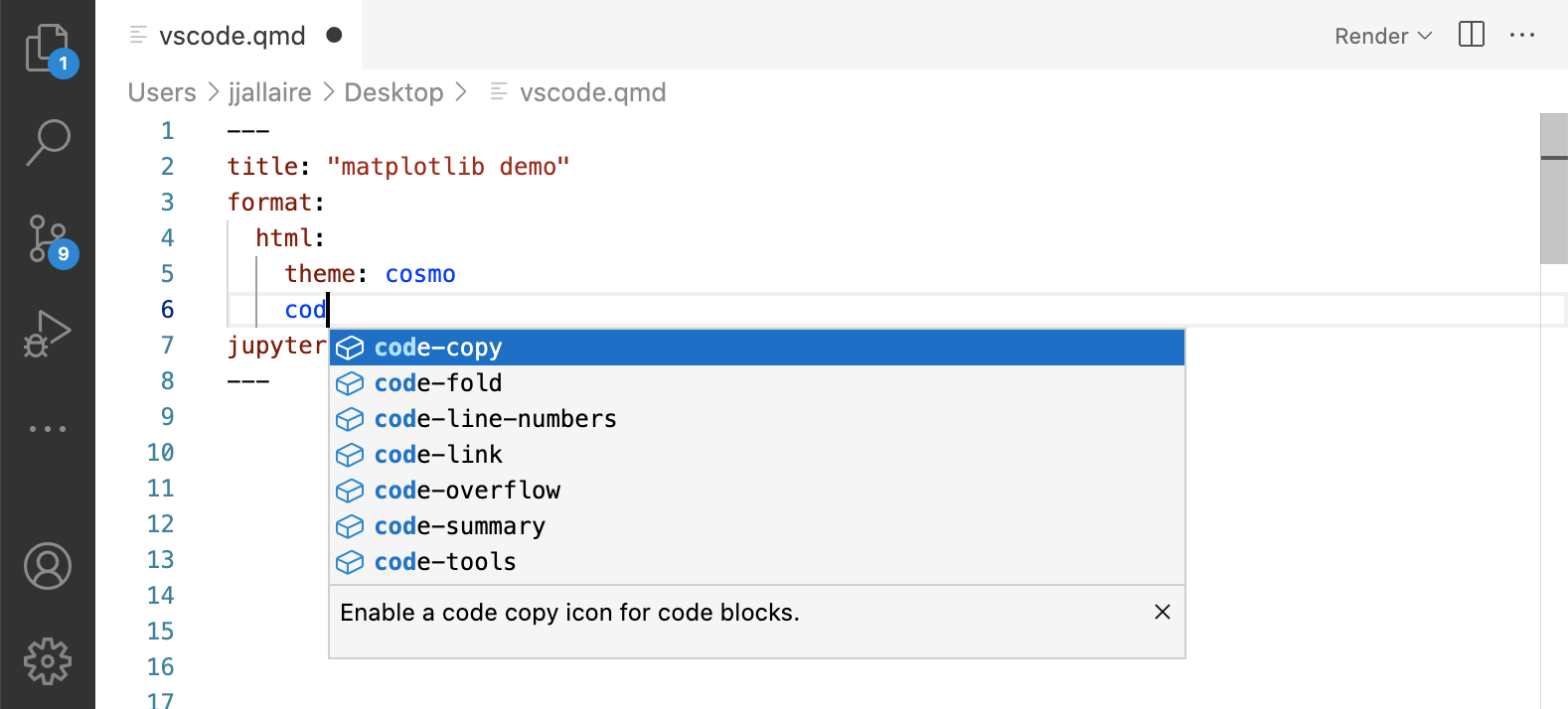
If you have incorrect YAML it will also be highlighted when documents are saved:
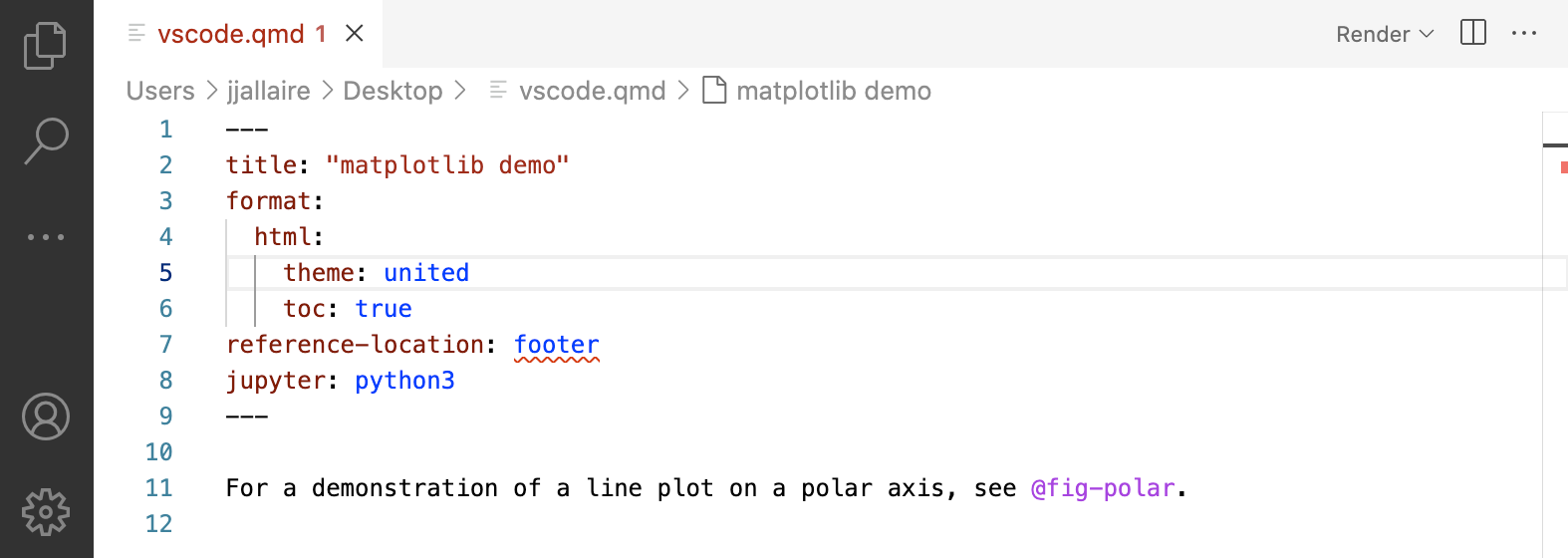
Note that YAML intelligence features require version 0.9.44 or later of the Quarto CLI.
Code Snippets
Code snippets are templates that make it easier to enter repeating code patterns (e.g. code blocks, callouts, divs, etc.). Execute the Insert Snippet command within a Quarto document to insert a markdown snippet:
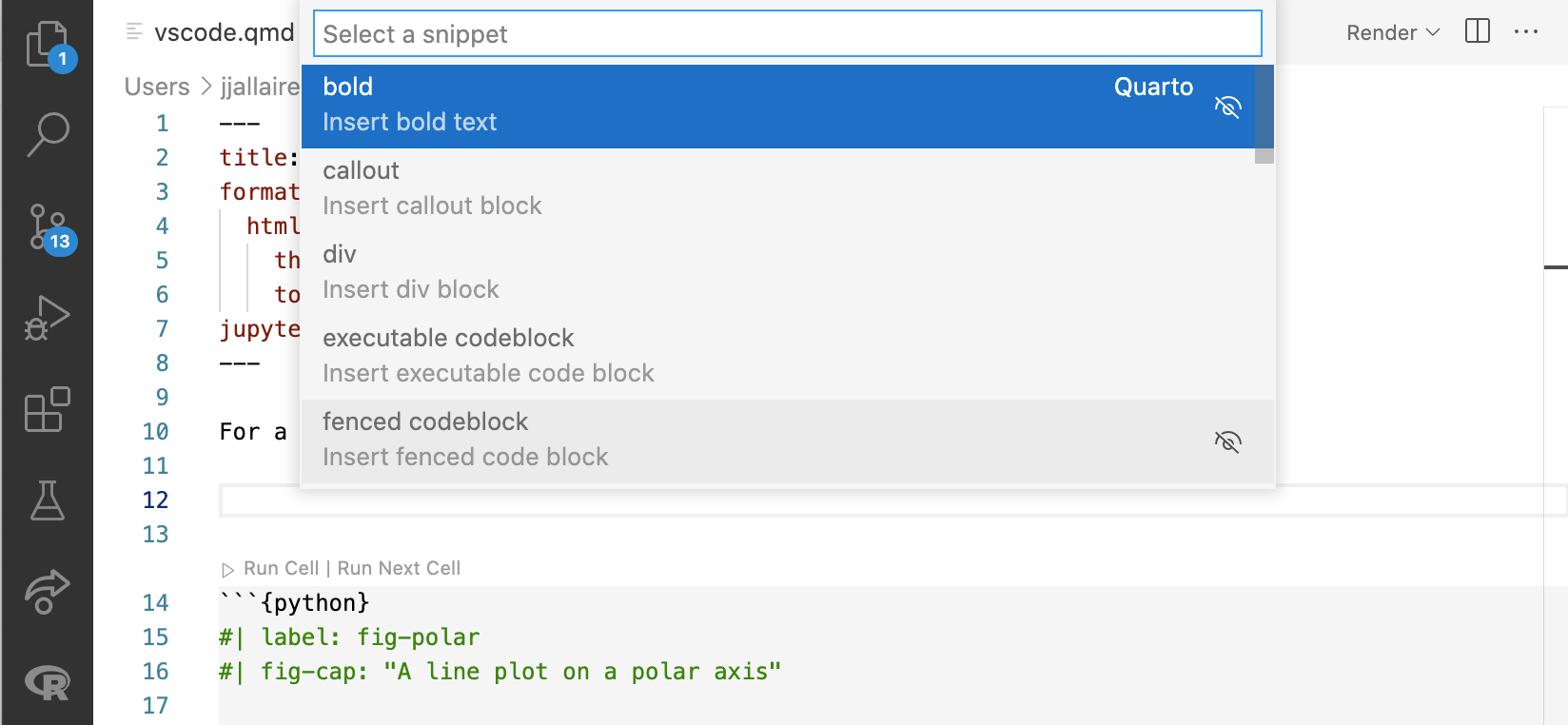
Notebook Editor
In addition to editing Quarto document as plain-text .qmd files, you can also use the VS Code Notebook Editor to author .ipynb notebooks that are rendered with Quarto. Next we’ll review the basics of editing .ipynb notebooks for use with Quarto.
YAML Front Matter
The first cell of your notebook should be a Raw cell that contains the document title, author, and any other options you need to specify. Note that you can switch the type of a call to Raw using the cell type menu at the bottom right of the cell:
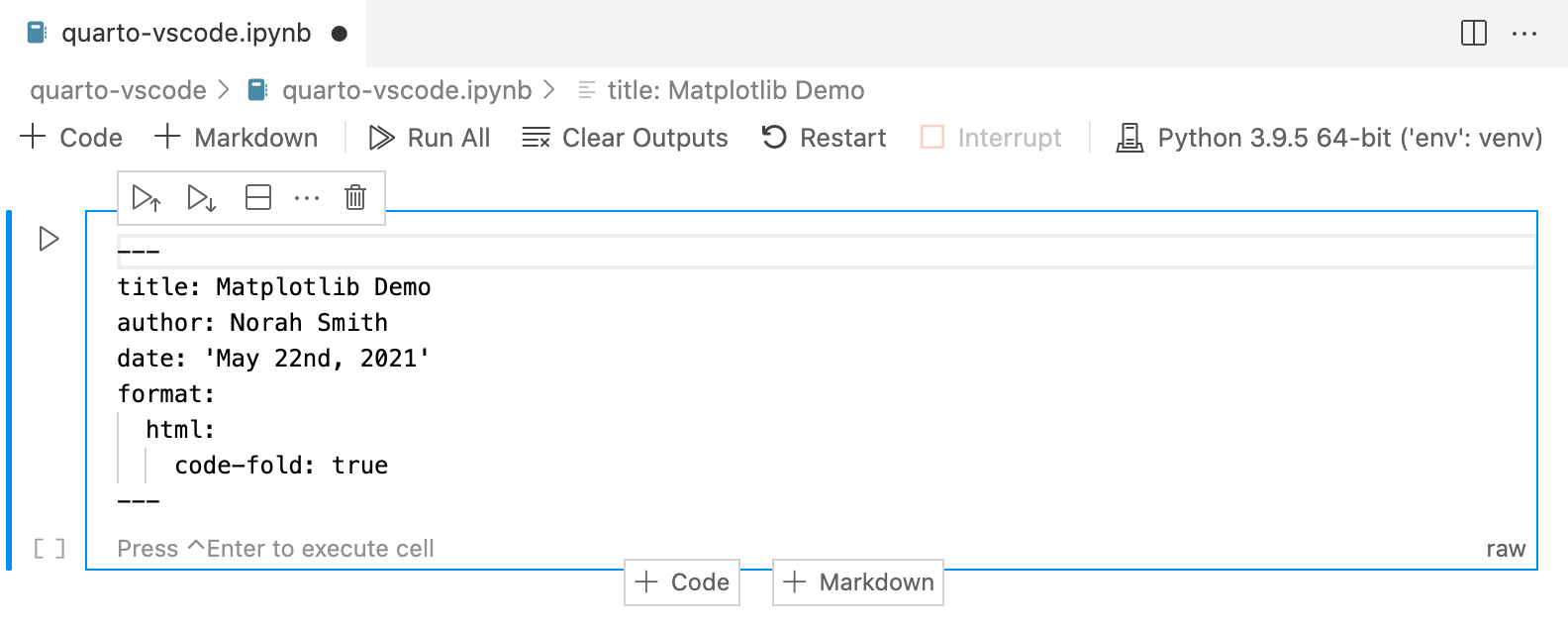
In this example we specify that we want code to appear collapsed by default. There are YAML options to control many other aspects of document rendering. See the documentation on Authoring and Output Formats for additional details.
Markdown Cells
Here’s the underlying code for the markdown cell:
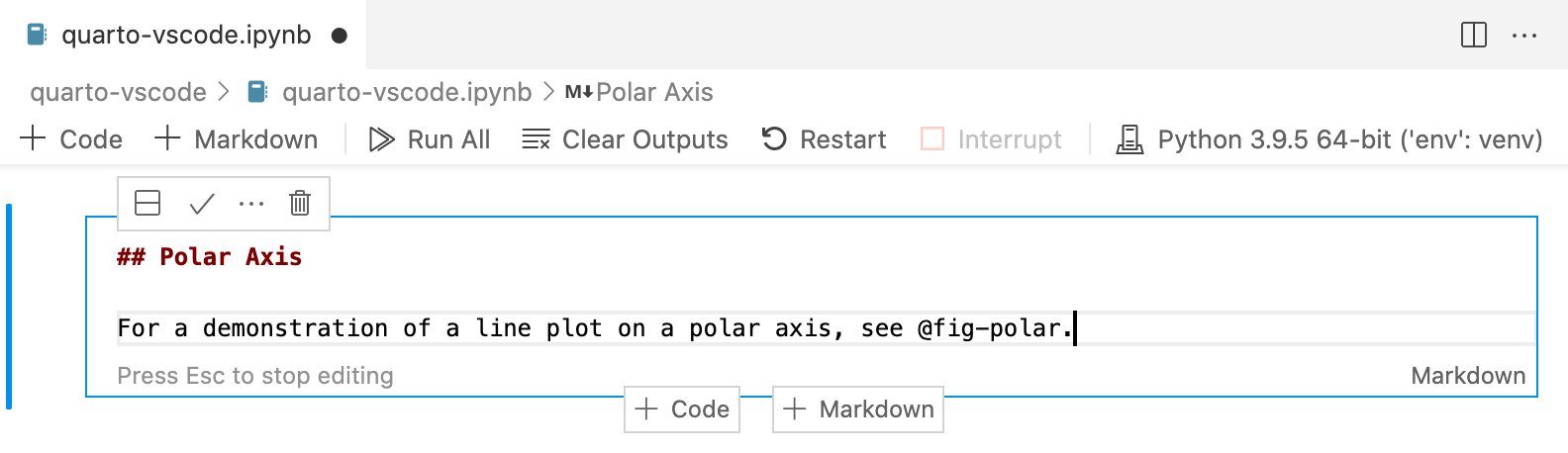
Note that a Quarto cross-reference (@fig-polar) is included in the markdown. Any valid Pandoc markdown syntax can be included in markdown cells.
Output Options
Quarto uses leading comments with a special prefix (#|) to denote cell options. Here we specify the label and fig-cap options so that the plot generated from the cell can be cross-referenced.
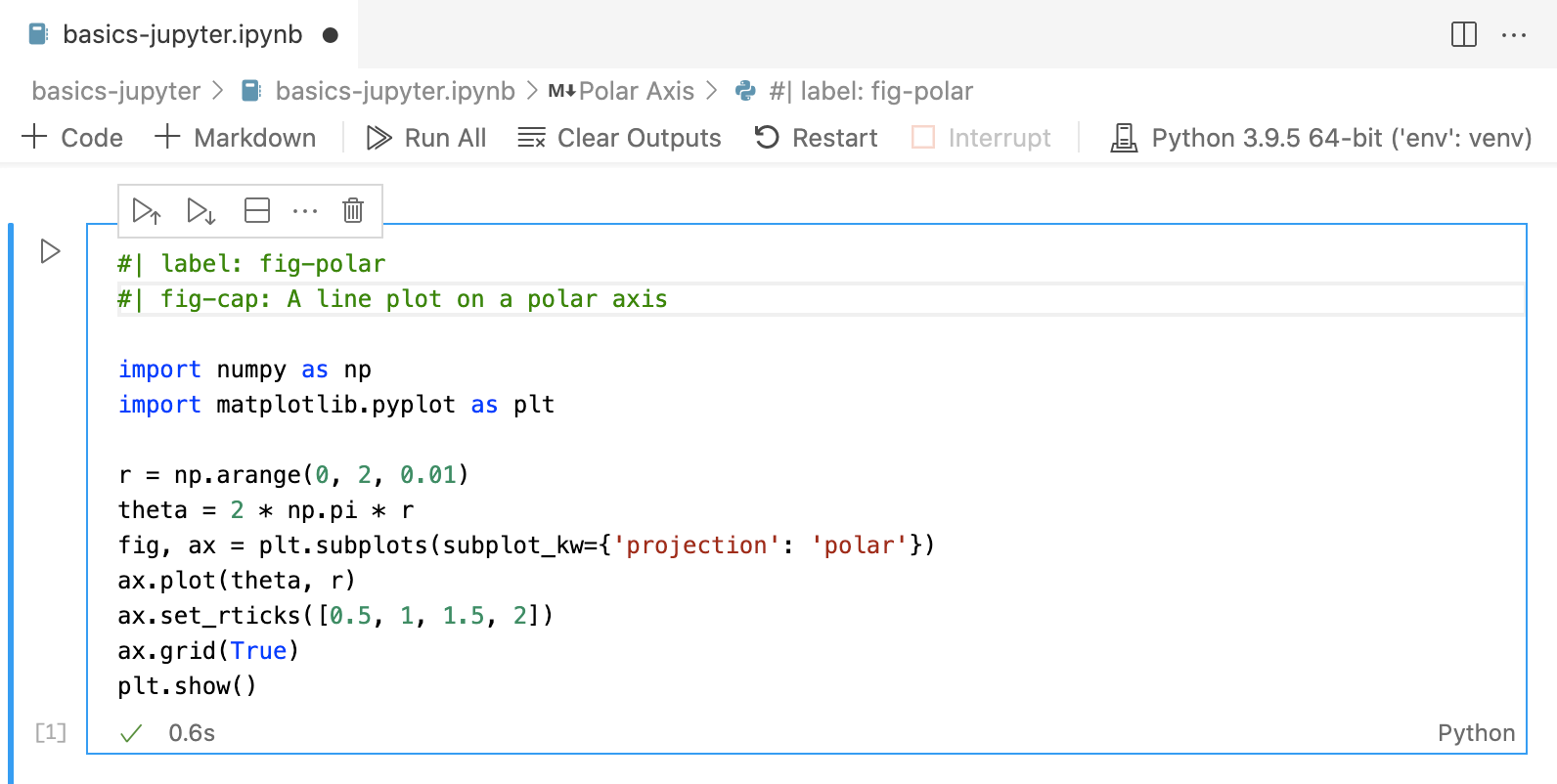
Note that options must appear at the very beginning of the cell. As with document front-matter, option names/values use YAML syntax.
There are many output options available, including options to optionally hide code, warnings, and/or output. See the documentation on Output Outputs for additional details.
Cell Execution
Note that when rendering an .ipynb Quarto will not execute the cells within the notebook by default (the presumption being that you already executed them while editing the notebook). If you want to execute the cells you can pass the --execute flag to render:
quarto render notebook.ipynb --executeYou can also specify this behavior within the notebook’s YAML front matter:
---
title: "My Notebook"
execute:
enabled: true
---There are many other execution options available (e.g. to control caching, optimizing kernel start-up time, etc.). Learn more about these options in Execution Options.
Converting Notebooks
You can convert between .ipynb and .qmd representations of a notebook using the quarto convert command. For example:
quarto convert basics-jupyter.ipynb
quarto convert basics-jupyter.qmdSee quarto convert help for additional details on converting notebooks.